In the if statement case, if the condition is true then the block if will be executed but for the false condition, we have no specific block. Programmers want to execute some different cases or some different statements if the condition is false. This limitation can be removed by using an if else in Java.
What is if else in Java?
Condition is checked in the if-else statement. If the condition is true then the if block is executed and if the condition is false then else block is executed.
Syntax:
if (condition) {
//if the condition is true then if block executed
} else {
//if the condition is false then else block executed }Java if else Flowchart
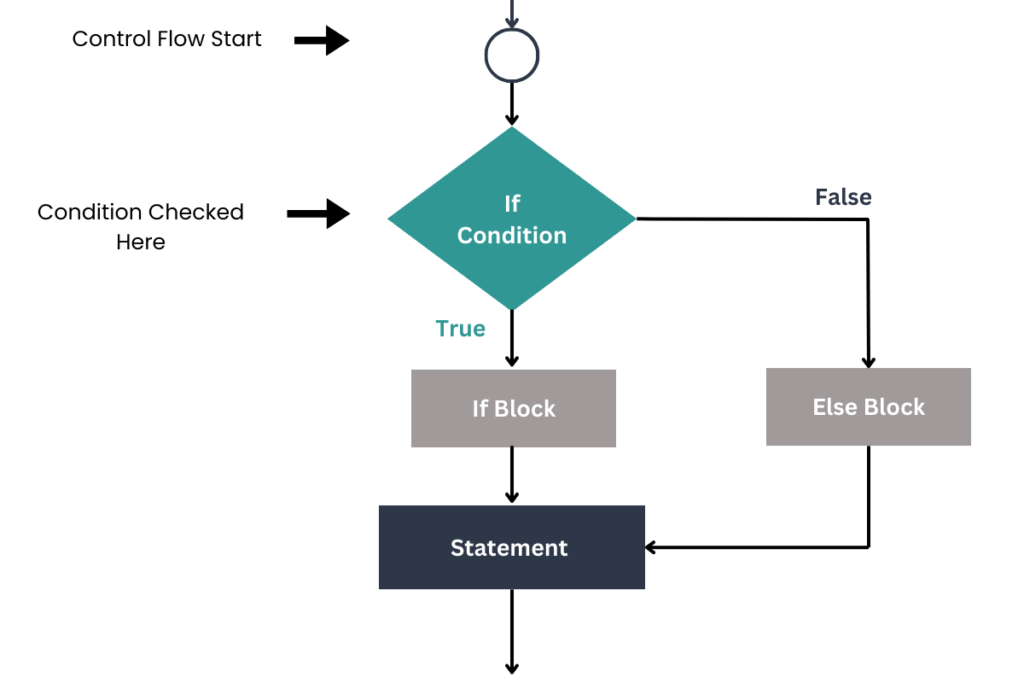
Explanation:
Let’s understand the if-else statement working with the help of a flowchart. First control start and go towards if condition.
If the condition is true then the body if will be executed and after the execution of if block, control will be transferred to the next statements in a program.
Suppose the condition is false then the else body will be executed and after the execution of else block, control will be transferred to the next statements in a program.
Java if else program
int codeNumber = 45 ;
if (codeNumber >= 0) {
System.out.println("The codeNumber is positive.");
} else {
System.out.println("The codeNumber is negative.");
}
Explanation:
- Variable name is
codeNumberand value is45. - The first condition
(codeNumber >= 0)is checked. In this programcodeNumbervalue is45. - So, this condition
(codeNumber >= 0)is true andifblock will be executed. - Output is
The codeNumber is positive.
Output:
The codeNumber is positive.Suppose, codeNumber value is -45 then what will be the output?
int codeNumber = -45 ;
if (codeNumber >= 0) {
System.out.println("The codeNumber is positive.");
} else {
System.out.println("The codeNumber is negative.");
}
Explanation:
- Variable name is
codeNumberbut now the value is –45. - The first condition
(codeNumber >= 0)is checked. In this programcodeNumbervalue is –45. - So, this condition
(codeNumber >= 0)is false and nowelseblock will be executed. - Output is
The codeNumber is negative.
Output:
The codeNumber is negative.The Shorthand if-else
Java provides a short way to write if-else statement with the help of a ternary operator.
The ternary operator also called the conditional operator takes three operands.
Most of the developers use a ternary operator instead of if-else.
Java short if else syntax
variable = (condition) ? expression1 : expression2;
- condition: The condition to evaluate.
- expression1: The value assigned to the variable if the condition is true.
- expression2: The value assigned to the variable if the condition is false.
let’s try to make the above codeNumber program with ternary operator.
Program with a Ternary operator
int codeNumber = -45;
String result = (codeNumber >= 0) ? "The codeNumber is positive." : "The codeNumber is negative.";
System.out.println(result);
Here, the ternary operator checks if codeNumber is greater than or equal to 0. If true, it assigns the message “The codeNumber is positive.” to the result variable; otherwise, it assigns “The codeNumber is negative.” The result is then printed.
Common Mistakes
Confusing Assignment with Equality:
A common mistake is confusing the assignment operator = with the equality operator ==. This can lead to unintended assignments and logical errors.
Incorrect:
if (number = 0) { // This assigns 0 to number, instead of checking equality
System.out.println("The number is zero.");
}
Correct:
if (number == 0) {
System.out.println("The number is zero.");
}
Programming Tips
When using the if-else statement, always ensure your conditions are specific and well-defined to avoid unexpected behavior in your program. For complex conditions, break them down into multiple if-else statements for clarity.
Conclusion
Mastering the if-else statement in Java is a fundamental skill that allows you to control the flow of your program based on specific conditions. Whether you’re handling basic logic or more complex decisions, understanding how to use if-else effectively will make your code more dynamic and responsive. Keep practicing, and you’ll find that these concepts become second nature in no time!



